Energy-dependent normalization
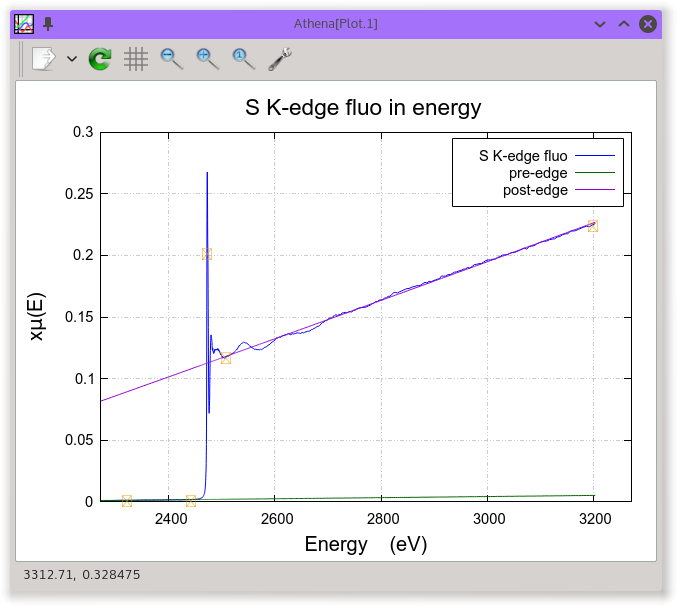
When measuring fluorescence data at low energy, the data might have an
unusual overall shape as shown in the S K-edge data in the figure
below. This behavior is due to the energy dependence of the signal on
the gas-filled I₀ chamber.
As the energy of the incident beam increases, the absorption of the
gasses in I₀ significantly decreases. Since the fluorescence
signal if If/I₀, the μ(E) grows with energy. Since the
edge-step normalization of the data is made by dividing out a constant
edge-step value, the energy-dependence of I₀ results in a χ(k)
signal that is somewhat amplified.
This amplification effect can be approximately corrected by an
energy-dependent normalization. This is implemented using the pre-
and post-edge lines. A function is computed as the difference between
the post-edge and pre-edge lines. This difference function, which
will be positive definite so long as the pre- and post-edge lines are
well-behaved, is multiplied by μ(E) before performing the
background removal.
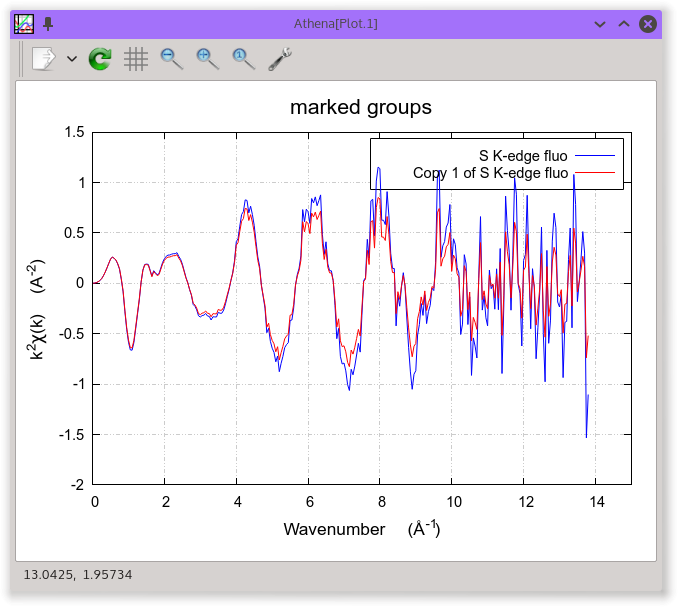
The resulting corrected χ(k) is shown as the red trace in the
right-hand figure above. The correction is small, but might
contribute to the accuracy of an EXAFS analysis.
 This sort of correction is only valid for low-energy EXAFS data
measured in fluorescence. Using this tool incorrectly can damage your
χ(k) data in a way that is difficult to understand after the fact.
Also, using this tool with poorly chosen pre- or post-edge lines will
damage the data. It is up to you to be sure
those lines are chosen sensibly.
This sort of correction is only valid for low-energy EXAFS data
measured in fluorescence. Using this tool incorrectly can damage your
χ(k) data in a way that is difficult to understand after the fact.
Also, using this tool with poorly chosen pre- or post-edge lines will
damage the data. It is up to you to be sure
those lines are chosen sensibly.
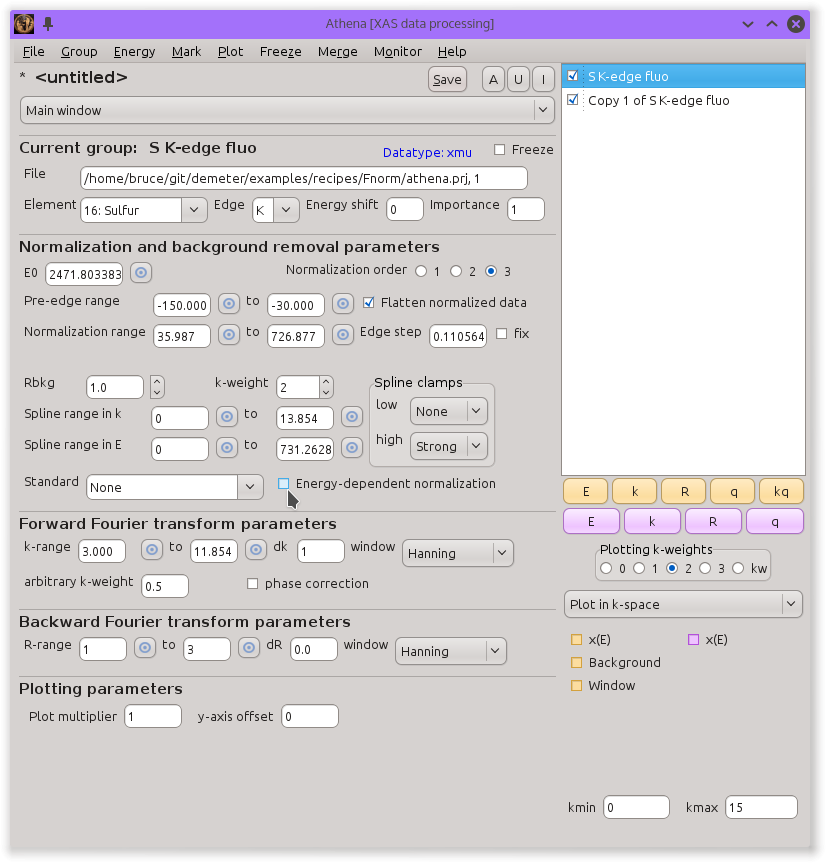
The control for this energy-dependent normalization is the checkbutton
near the bottom of the background removal section of controls, as seen
in the following screenshot.
This control is normally disabled. To enable it, you must toggle on the
♦Athena → show_funnorm
configuration parameter.
If you import a project file which has one or more groups using the
energy-dependent normalization, then the control will be turned on automatically.
 Enabling this feature makes project files for both ATHENA and
ARTEMIS incompatible with versions before 0.9.23. If you want to
use this feature and share your project files with others who are
using older version of the software, they will not be able to import
your project files.
Enabling this feature makes project files for both ATHENA and
ARTEMIS incompatible with versions before 0.9.23. If you want to
use this feature and share your project files with others who are
using older version of the software, they will not be able to import
your project files.
 Another word of caution about using this feature of ATHENA. When
you make a plot in energy, the function that gets plotted is μ(E)
and it's background, not the corrected
μ(E) and it's background. However, χ(k), χ(R), and
χ(q) are made from the corrected μ(E). It is possible,
paticularly for especially noisy data, that the background removal
displayed for the raw μ(E) will be substantively different from the
background calculated for the corrected μ(E). Thus it is possible
that a plot in energy might look sensible, but the plot in k will be
garbage. Or vice-versa. Again, use this feature of ATHENA with
caution and foreknowledge.
Another word of caution about using this feature of ATHENA. When
you make a plot in energy, the function that gets plotted is μ(E)
and it's background, not the corrected
μ(E) and it's background. However, χ(k), χ(R), and
χ(q) are made from the corrected μ(E). It is possible,
paticularly for especially noisy data, that the background removal
displayed for the raw μ(E) will be substantively different from the
background calculated for the corrected μ(E). Thus it is possible
that a plot in energy might look sensible, but the plot in k will be
garbage. Or vice-versa. Again, use this feature of ATHENA with
caution and foreknowledge.
![[Athena logo]](../../images/pallas_athene_thumb.jpg)
 This sort of correction is only valid for low-energy EXAFS data
measured in fluorescence. Using this tool incorrectly can damage your
χ(k) data in a way that is difficult to understand after the fact.
Also, using this tool with poorly chosen pre- or post-edge lines will
damage the data. It is up to you to be sure
those lines are chosen sensibly.
This sort of correction is only valid for low-energy EXAFS data
measured in fluorescence. Using this tool incorrectly can damage your
χ(k) data in a way that is difficult to understand after the fact.
Also, using this tool with poorly chosen pre- or post-edge lines will
damage the data. It is up to you to be sure
those lines are chosen sensibly.