15.8. Unique potential styles¶
Consider this atoms.inp file for sodium uranyl triacetate:
title = Templeton et al.
title = Redetermination and Absolute configuration of Sodium Uranyl(VI) triacetate.
title = Acta Cryst 1985 C41 1439-1441
space = P 21 3
a = 10.6890 b = 10.6890 c = 10.6890
alpha = 90.0 beta = 90.0 gamma = 90.0
core = U edge = L3 rmax = 7.0
shift 0.00000 0.00000 0.00000
atoms
! elem x y z tag occ.
U 0.42940 0.42940 0.42940 U 1.00000
Na 0.82860 0.82860 0.82860 Na 1.00000
O 0.33430 0.33430 0.33430 Oax 1.00000
O 0.52420 0.52420 0.52420 Oax 1.00000
O 0.38340 0.29450 0.61100 Oeq 1.00000
O 0.54640 0.24430 0.50070 Oeq 1.00000
C 0.47860 0.22600 0.59500 C 1.00000
C 0.50880 0.12400 0.68620 C 1.00000
This crystal has 4 elemental species distributed over 8 crystallographic positions. Two of the oxygen sites are the two oxygenyl sites with U-O double bond distance of about 1.76 Å. The remaining oxygen sites are single bonded at a distance of about 2.46 Å.
In the Atoms and Feff chapter, the concept of unique potential styles was introduced. Here we show examples of how these work using sodium uranyl triacetate.
15.8.1. Each element gets a unique potential¶
Choosing the elements style assigns a unique potenitial to
each atomic species in the crystal. Using this style results in the
following feff.inp file:
TITLE Templeton et al.
TITLE Redetermination and Absolute configuration of Sodium Uranyl(VI) triacetate.
TITLE Acta Cryst 1985 C41 1439-1441
HOLE 4 1.0 * FYI: (U L3 edge @ 17166 eV, second number is S0^2)
* mphase,mpath,mfeff,mchi
CONTROL 1 1 1 1
PRINT 1 0 0 0
RMAX 5.0
*NLEG 4
POTENTIALS
* ipot Z tag
0 92 U
1 92 U
2 11 Na
3 8 O
4 6 C
ATOMS * this list contains 81 atoms
* x y z ipot tag distance
0.00000 0.00000 0.00000 0 U 0.00000
1.01332 1.01332 1.01332 3 Oax.1 1.75512
-1.01652 -1.01652 -1.01652 3 Oax.2 1.76067
1.25061 -1.97853 0.76213 3 Oeq.1 2.46160
-1.97853 0.76213 1.25061 3 Oeq.1 2.46160
... (more atoms follow)
This is reasonable input for FEFF. Indeed, for many crystals, the elements style is exactly what you want. With four elements in the cyrstal, five unique potentials are made. The absorber is always potential index 0. The remaining uranium atoms are given potential index 1.
For this material, it is probably a poor idea to give the axial (double bonded, distance 1.76 Å) and equatorial (single bonded, distance 2.46 Å) the same potential index. Doing so forces their muffin tin radii to be the same. Given this substantial difference in distance, it is probably a good idea to let the two types of oxygen atoms have different muffin tin radii so that their scattering amplitudes and phase shifts can be computed differently. That introduces a more chemically reasonable potential model.
15.8.2. Each tag gets a unique potential¶
The two oxygen types can get differnt unique potentials by choosing
the tags style. Note that, in the atoms.inp file,
pairs of oxygen sites were given the tags “Oax” and
“Oeq”. Also note that the two carbon sites were given the
same tag. With all this, we get the following feff.inp file:
TITLE Templeton et al.
TITLE Redetermination and Absolute configuration of Sodium Uranyl(VI) triacetate.
TITLE Acta Cryst 1985 C41 1439-1441
HOLE 4 1.0 * FYI: (U L3 edge @ 17166 eV, second number is S0^2)
* mphase,mpath,mfeff,mchi
CONTROL 1 1 1 1
PRINT 1 0 0 0
RMAX 5.0
*NLEG 4
POTENTIALS
* ipot Z tag
0 92 U
1 92 U
2 11 Na
3 8 O
4 8 O
5 6 C
ATOMS * this list contains 81 atoms
* x y z ipot tag distance
0.00000 0.00000 0.00000 0 U 0.00000
1.01332 1.01332 1.01332 3 Oax.1 1.75512
-1.01652 -1.01652 -1.01652 3 Oax.2 1.76067
1.25061 -1.97853 0.76213 4 Oeq.1 2.46160
-1.97853 0.76213 1.25061 4 Oeq.1 2.46160
... (more atoms follow)
Note that potential indeces 3 and 4 are both for oxygen atoms. 3 is for the short, axial oxygens and 4 is for the longer, equatorial oxygens.
15.8.3. Each site gets a unique potential¶
The final option for potential assignement is the sites style. In this style, each crystallographic position gets its own potential index.
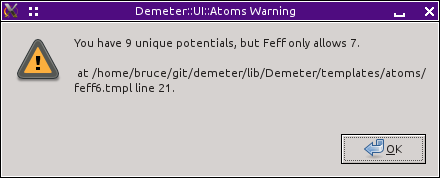
This is a somewhat dangerous option because FEFF only
allows up to 7 potentials beyond the absorber (for a total of 8). In
this crystal, we have 8 sites which results in 8 unique
potentials. The software dutifully writes out the feff.inp
file below, but it also issues this warning.
TITLE Templeton et al.
TITLE Redetermination and Absolute configuration of Sodium Uranyl(VI) triacetate.
TITLE Acta Cryst 1985 C41 1439-1441
HOLE 4 1.0 * FYI: (U L3 edge @ 17166 eV, second number is S0^2)
* mphase,mpath,mfeff,mchi
CONTROL 1 1 1 1
PRINT 1 0 0 0
RMAX 5.0
*NLEG 4
POTENTIALS
* ipot Z tag
0 92 U
1 92 U
2 11 Na
3 8 O
4 8 O
5 8 O
6 8 O
7 6 C
8 6 C
ATOMS * this list contains 81 atoms
* x y z ipot tag distance
0.00000 0.00000 0.00000 0 U 0.00000
1.01332 1.01332 1.01332 4 Oax.1 1.75512
-1.01652 -1.01652 -1.01652 3 Oax.2 1.76067
1.25061 -1.97853 0.76213 6 Oeq.1 2.46160
-1.97853 0.76213 1.25061 6 Oeq.1 2.46160
... (more atoms follow)
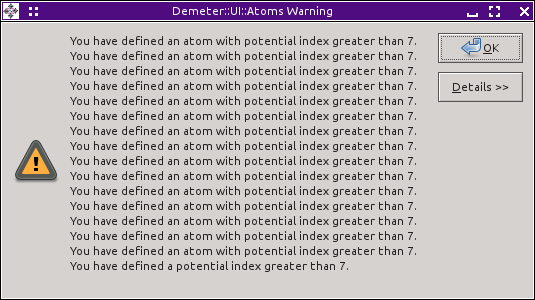
If you attempt to run FEFF with this input data, ARTEMIS will complain with the rather repetitious error message shown below and not run FEFF. You have to fix the FEFF input data either by hand-editing or by re-running ATOMS with a different potentials style.
DEMETER is copyright © 2009-2016 Bruce Ravel – This document is copyright © 2016 Bruce Ravel
This document is licensed under The Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License.
If DEMETER and this document are useful to you, please consider supporting The Creative Commons.